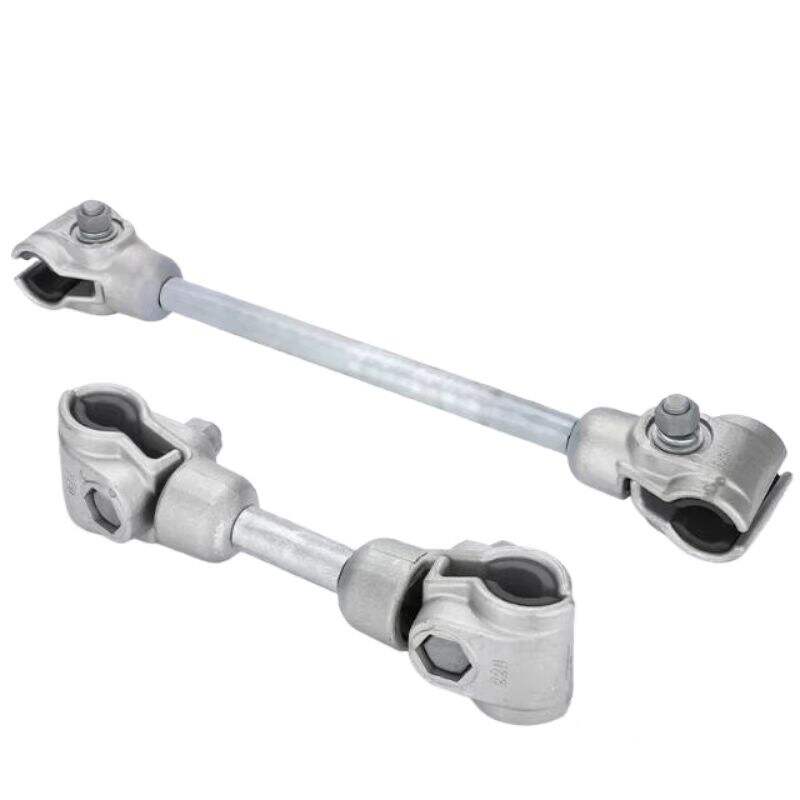
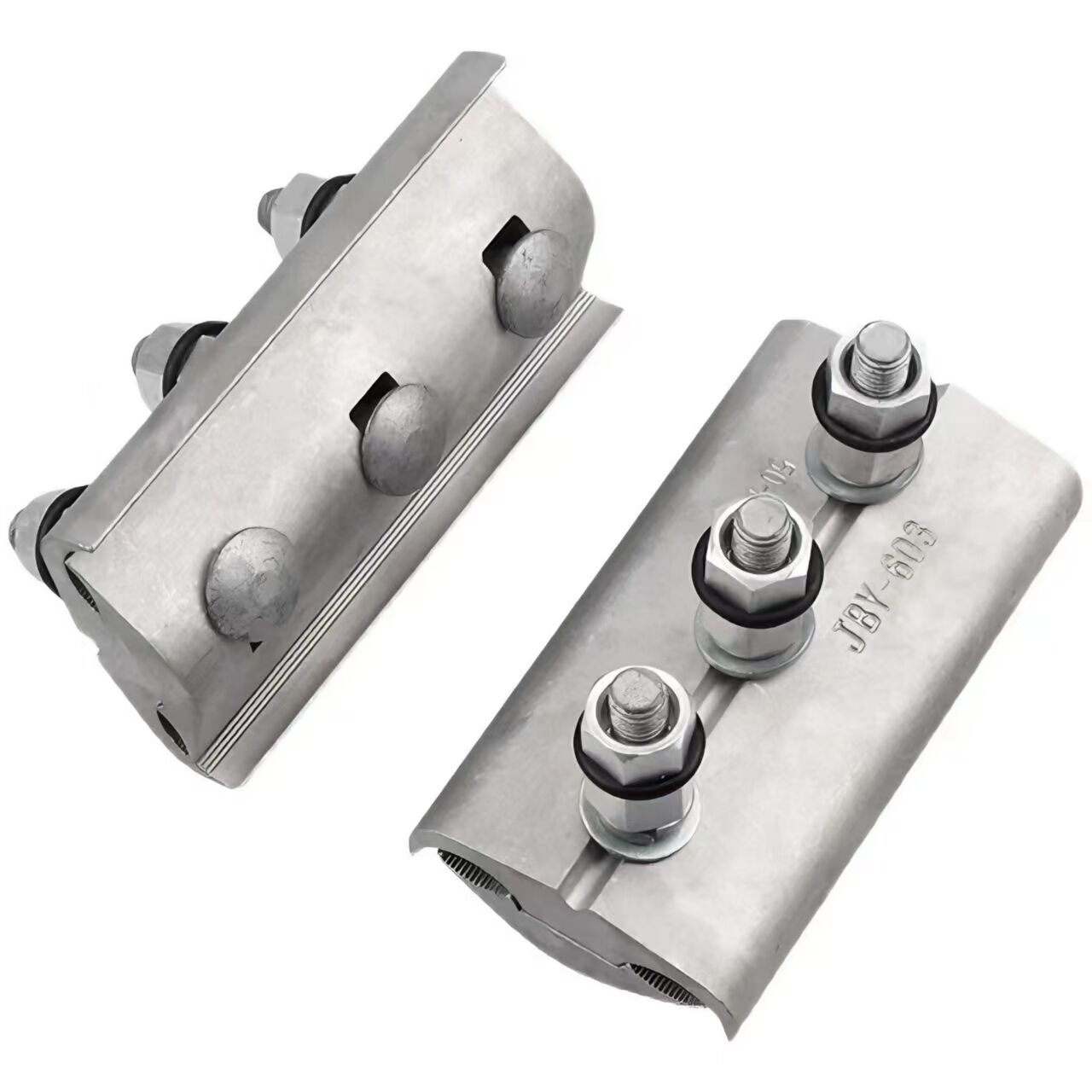
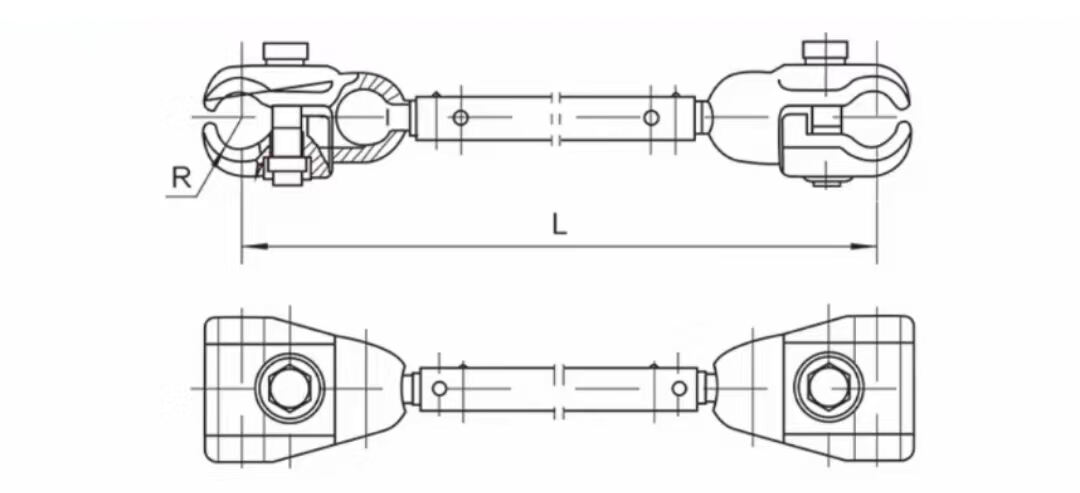
1. Maintaining Jumper Position
It keeps a safe distance between the jumper and the tower body, preventing collisions or contact that could cause arcs and short circuits. This mechanical separation is crucial for ensuring electrical insulation and avoiding catastrophic faults in high-voltage systems.
2. Tension Balancing
By balancing the tension of jumpers in each phase, it prevents excessive swinging caused by unbalanced tension, which could lead to jumper damage or breakage. This function stabilizes the mechanical state of the jumper, reducing stress on connection points and extending service life.
3. Wind Deflection Angle Limitation
It restricts the wind deflection angle of jumpers, ensuring that the swing amplitude under wind load does not exceed specified limits. This prevents collisions between jumpers and surrounding objects (e.g., tower structures, other conductors), maintaining the geometric stability of the line under dynamic loads.
4. Auxiliary Installation and Maintenance
During installation and maintenance, it can be used as a temporary tool to fix jumpers, facilitating operator handling. This feature improves construction efficiency by providing a stable anchor point for adjusting jumper position and tension, while reducing the risk of high-altitude operation accidents.
 E-mail:
E-mail: