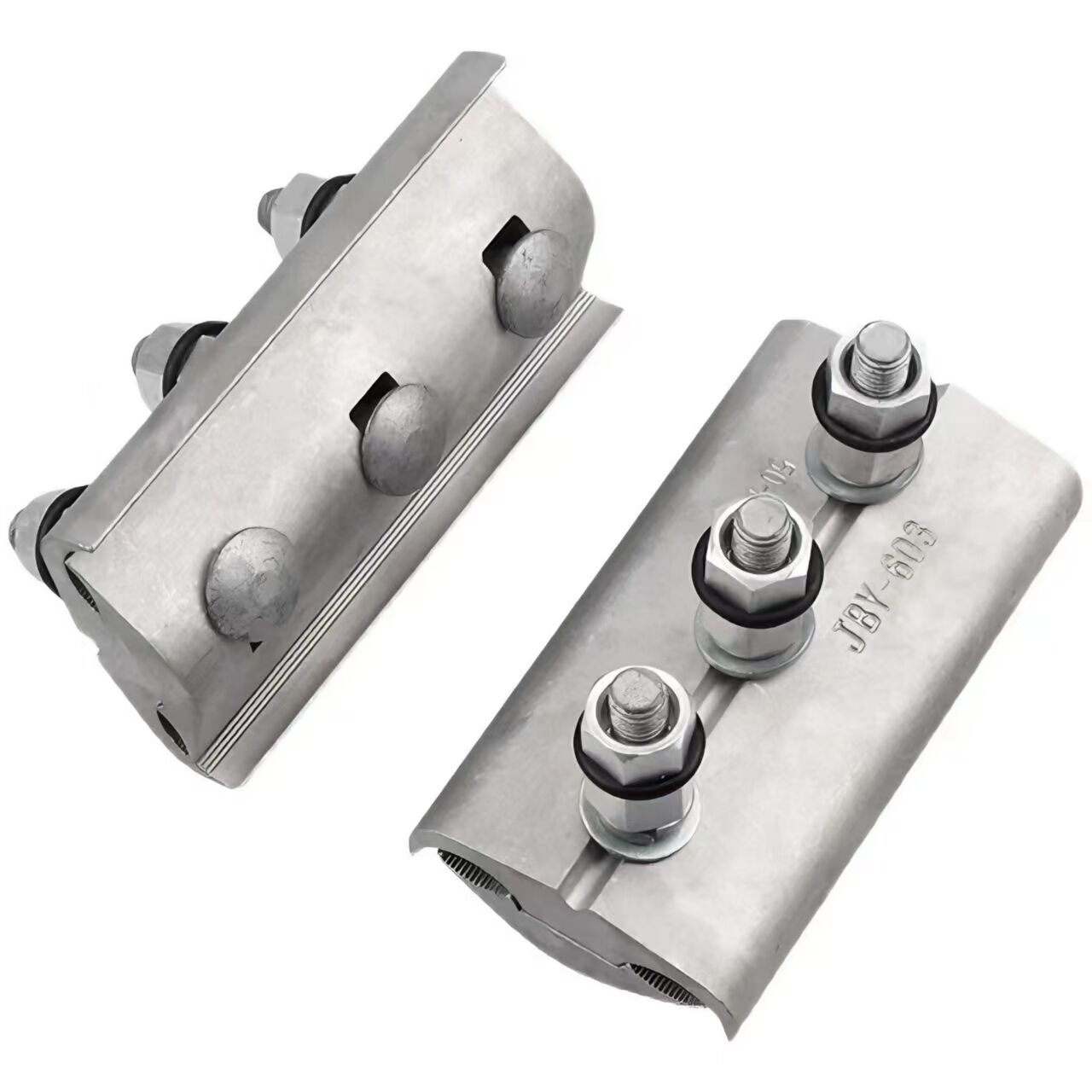
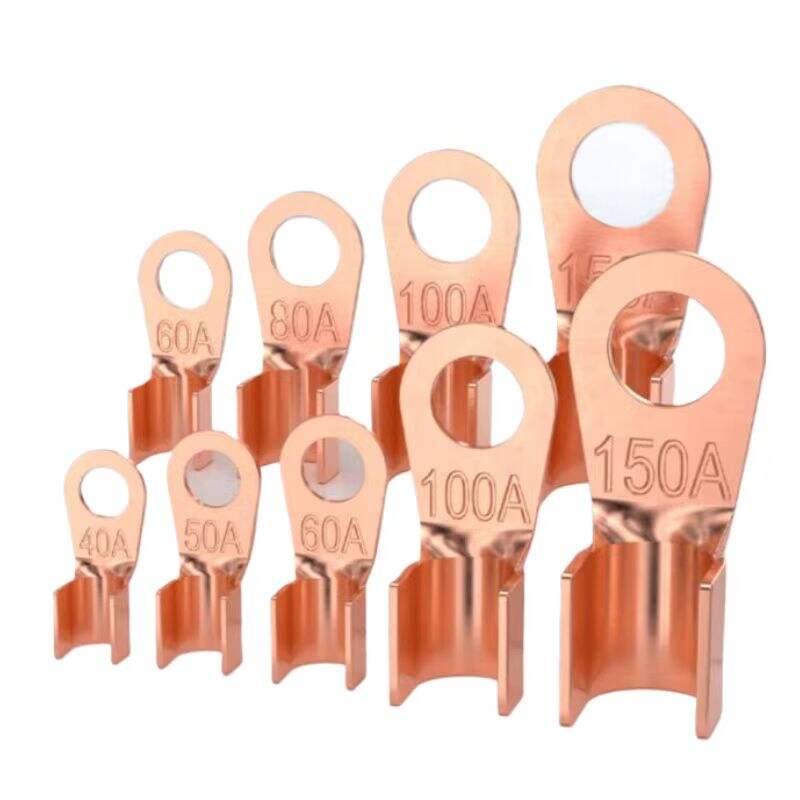
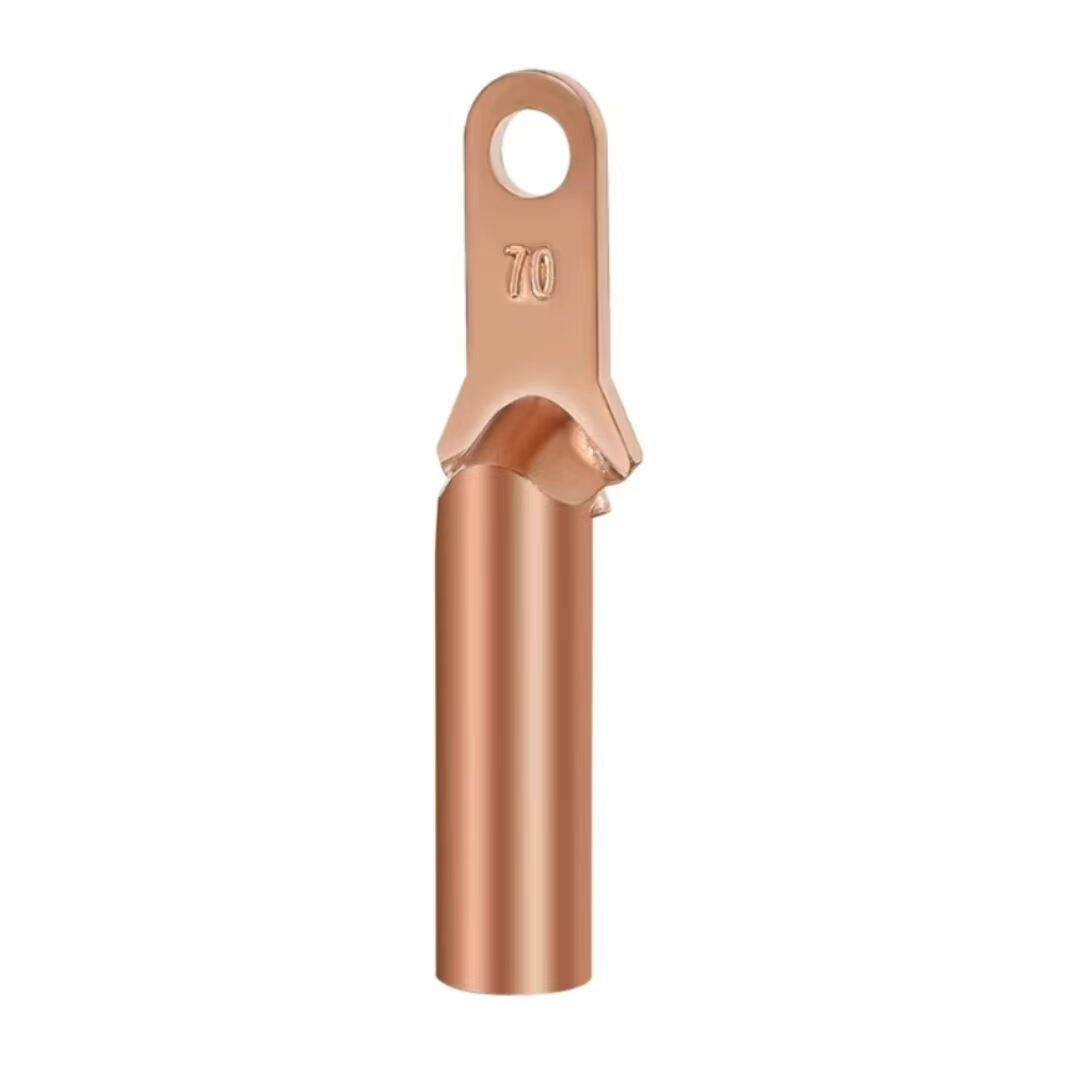
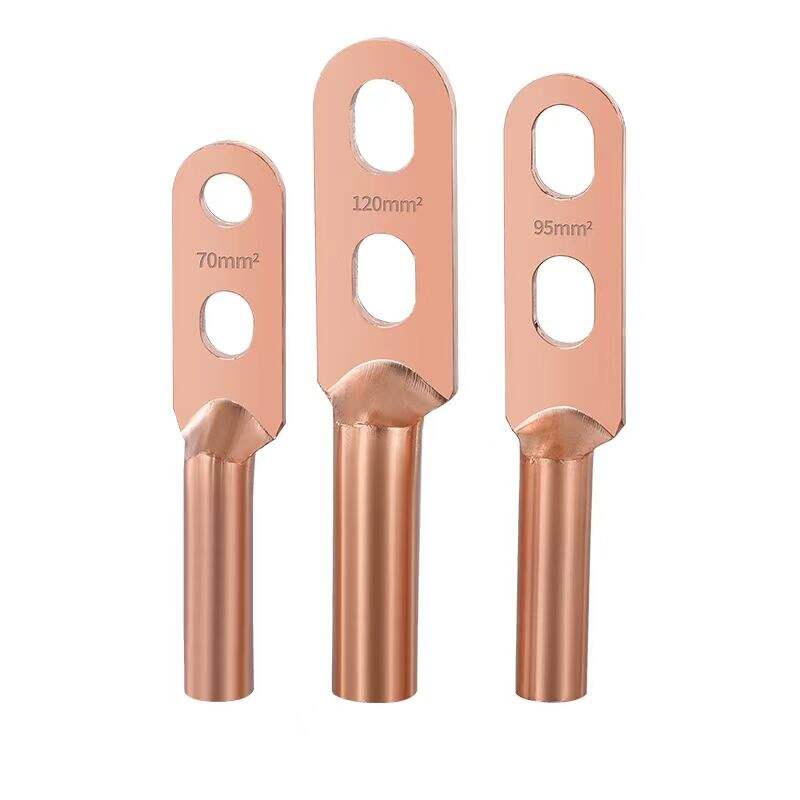
1. High-Quality Materials
Typically made of hot-dip galvanized steel or other conductive metal materials. The hot-dip galvanizing process forms a dense zinc layer on the surface, effectively preventing rust and corrosion of the steel, adapting to various harsh outdoor environments, and prolonging service life. This anti-corrosion treatment ensures the clamp remains structurally sound in extreme weather conditions, such as high humidity, salt mist, or industrial pollution.
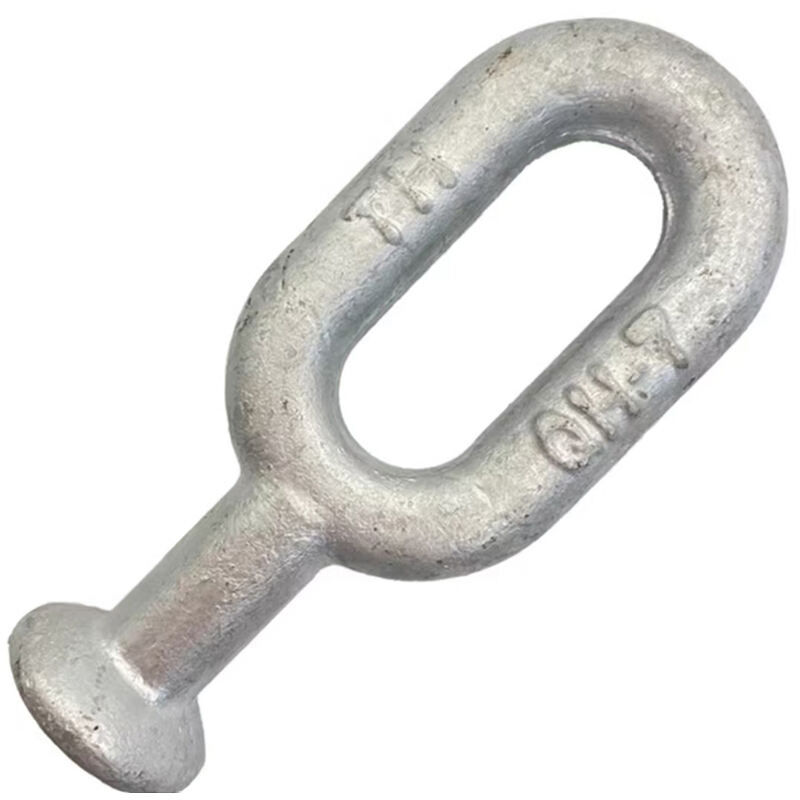
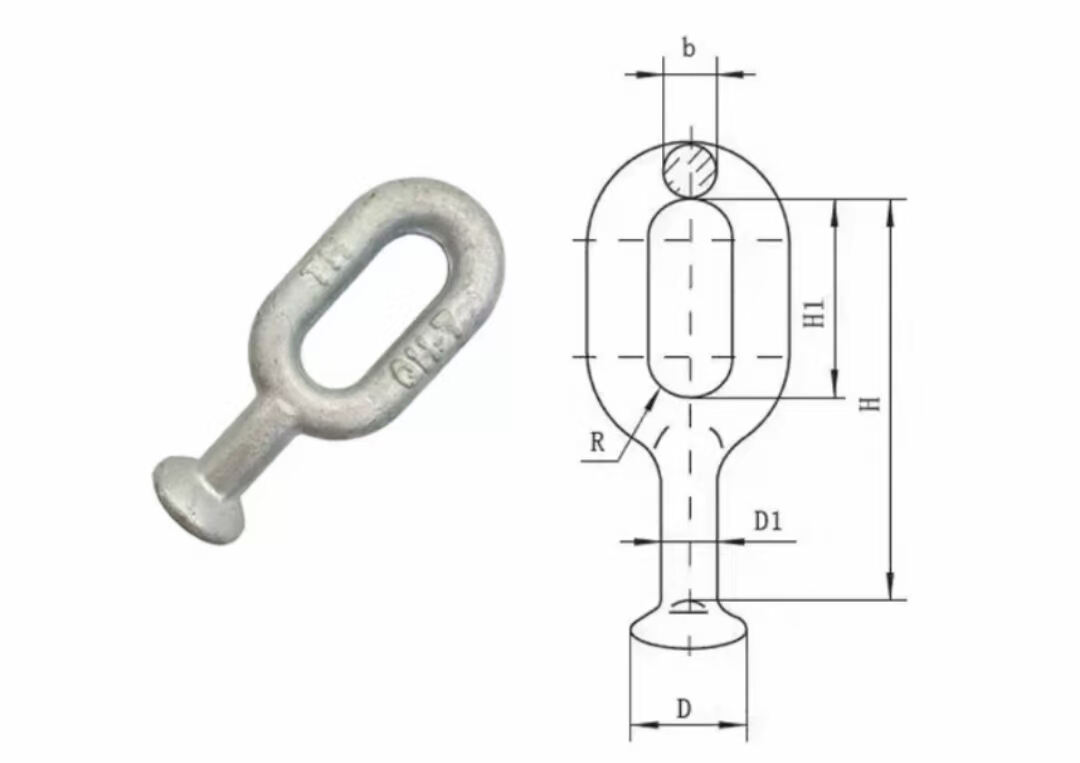
2. Rational Structure
One end is designed in a ball-head shape, which has excellent adaptability for connecting with insulator strings, ensuring a tight and secure connection that is not easy to detach. The other end is a ring-shaped joint, which can be fixed to utility poles or towers through right-angle suspension plates or similar fittings. This modular design facilitates quick assembly and ensures mechanical stability in both tension and compression scenarios.
3. High Strength
The selected steel undergoes a reasonable heat treatment process, giving it good strength and toughness. It can withstand substantial tensile forces, meeting the mechanical requirements of transmission lines during operation and ensuring reliable connections. For example, standard models can typically bear tensile loads ranging from 70 kN to 210 kN, making them suitable for various voltage classes from medium to ultra-high voltage systems.
 E-mail:
E-mail: