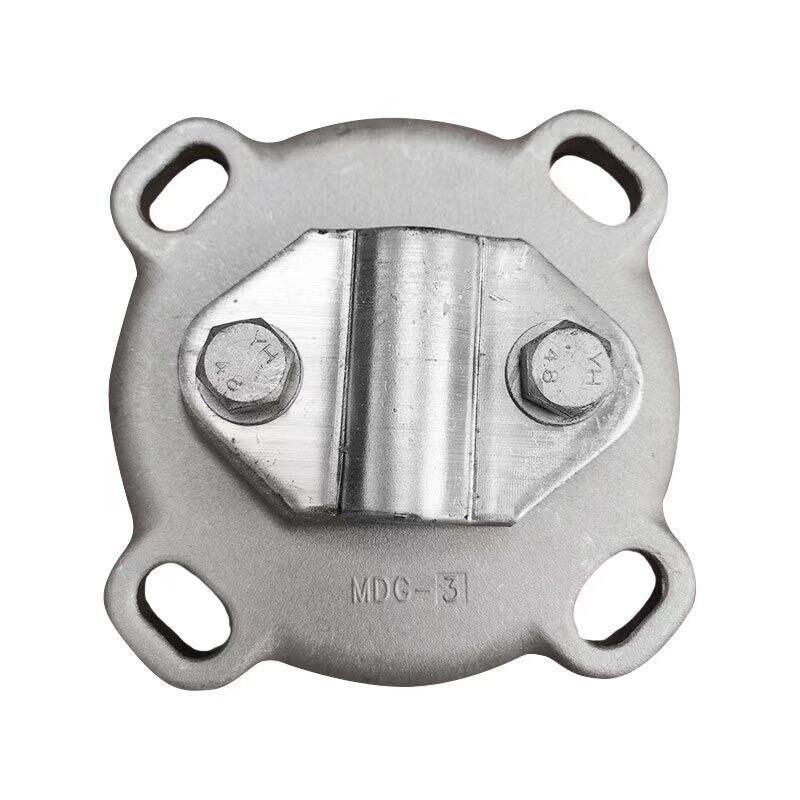
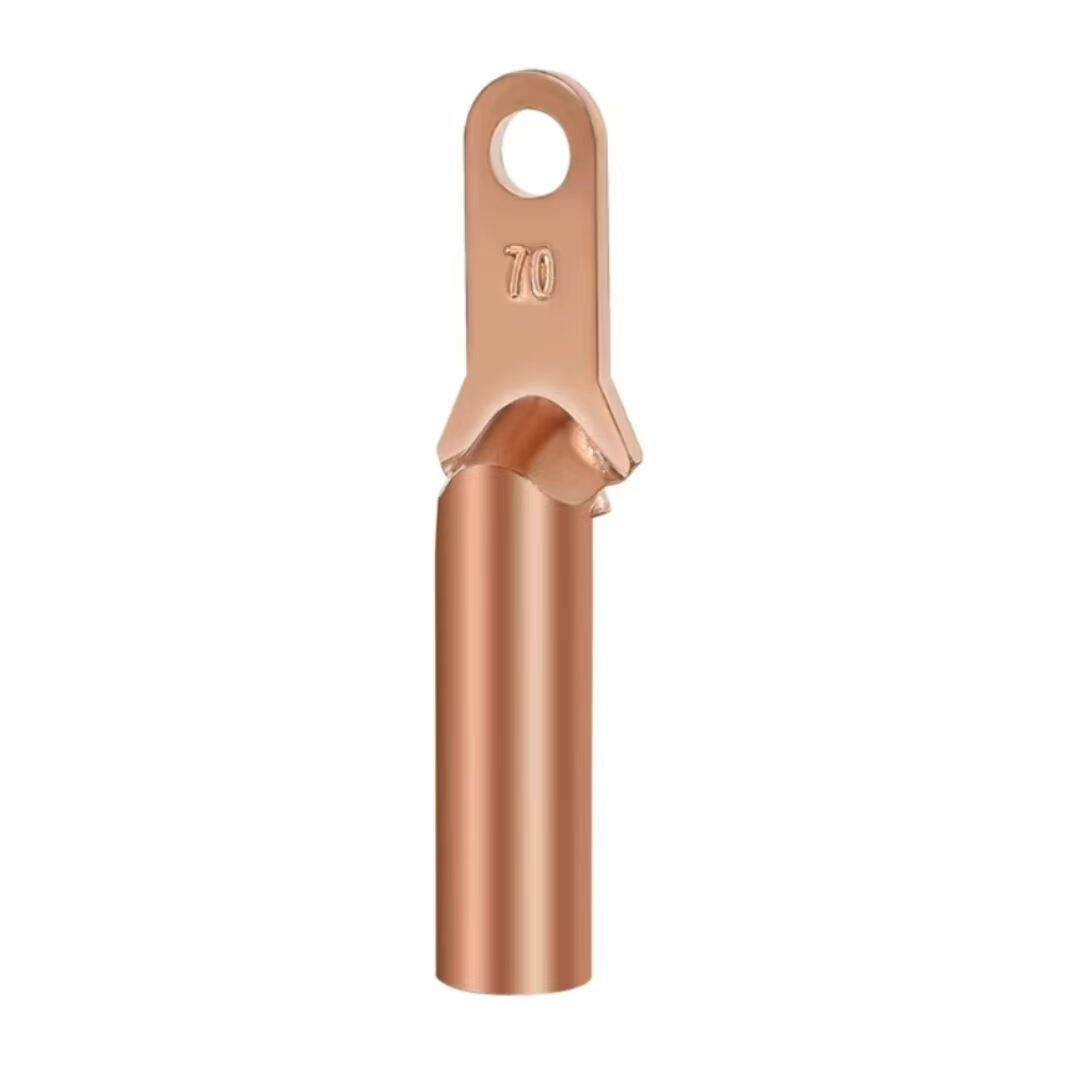
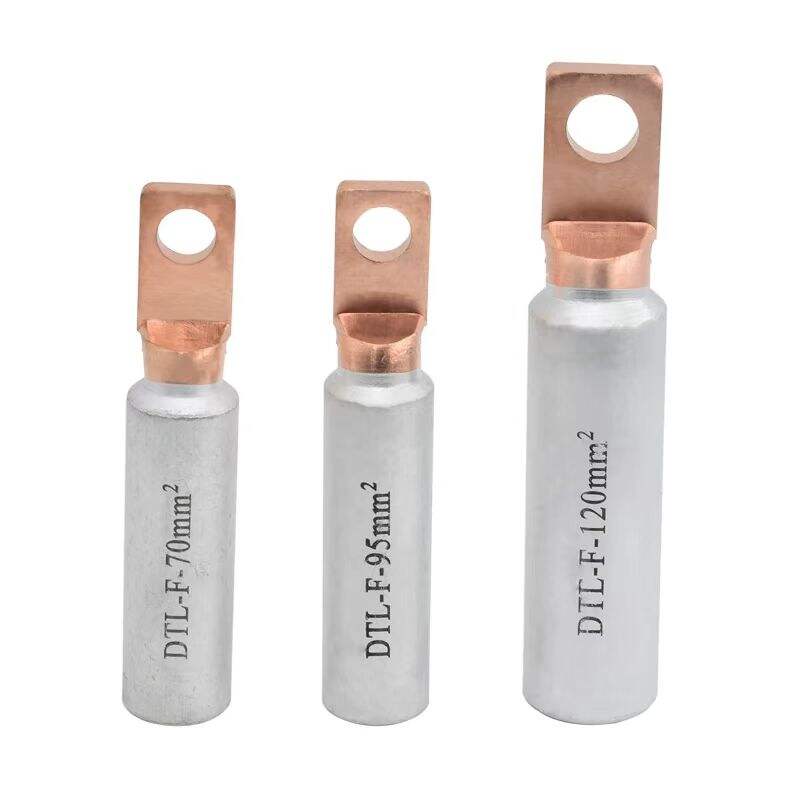
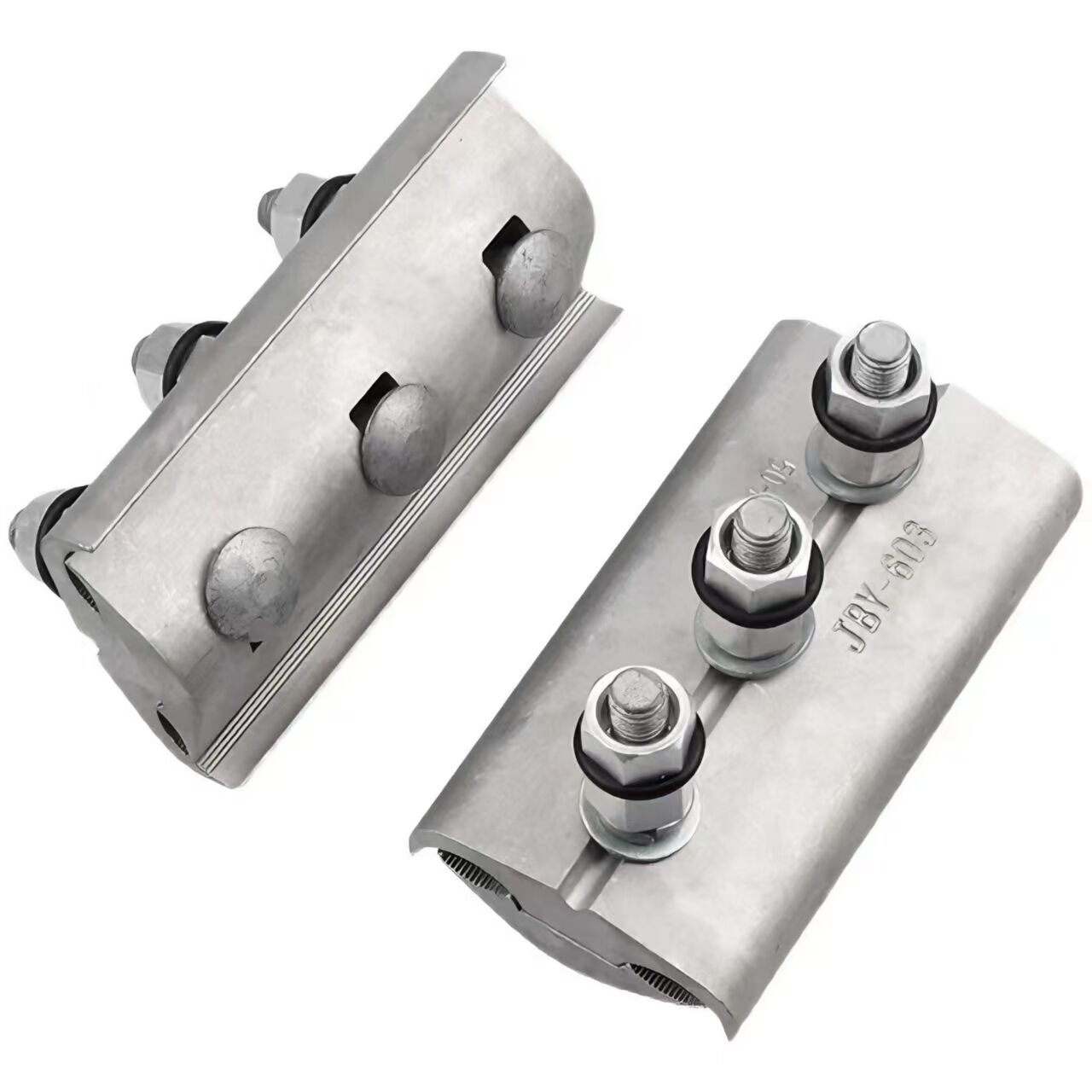
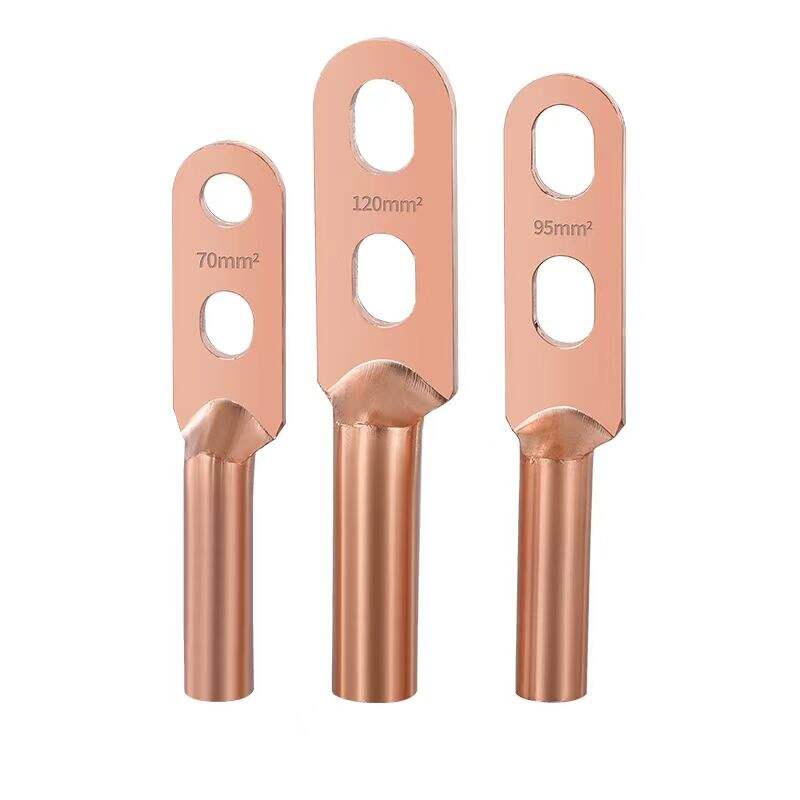
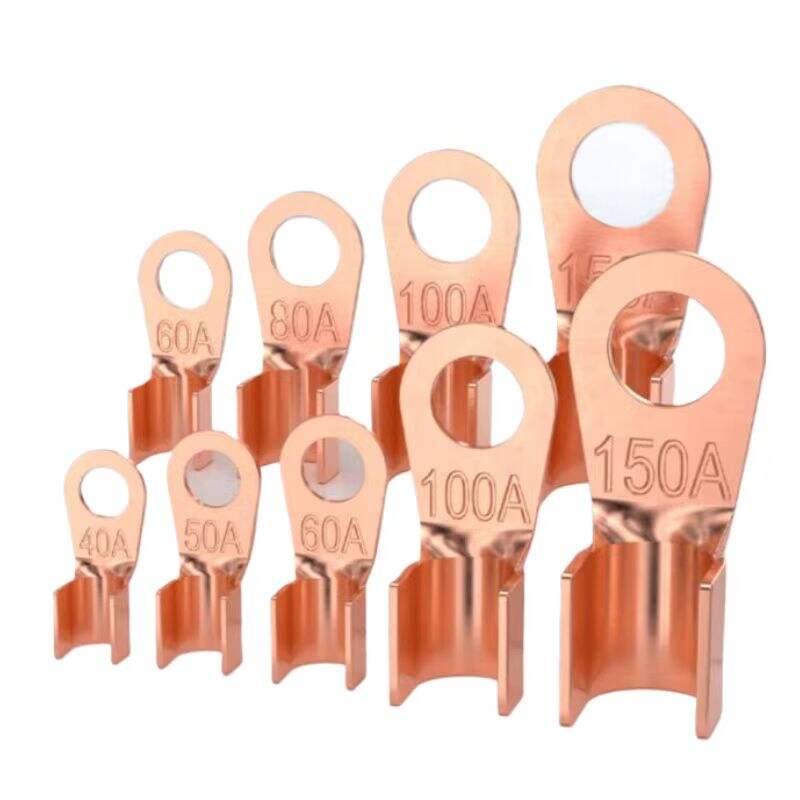
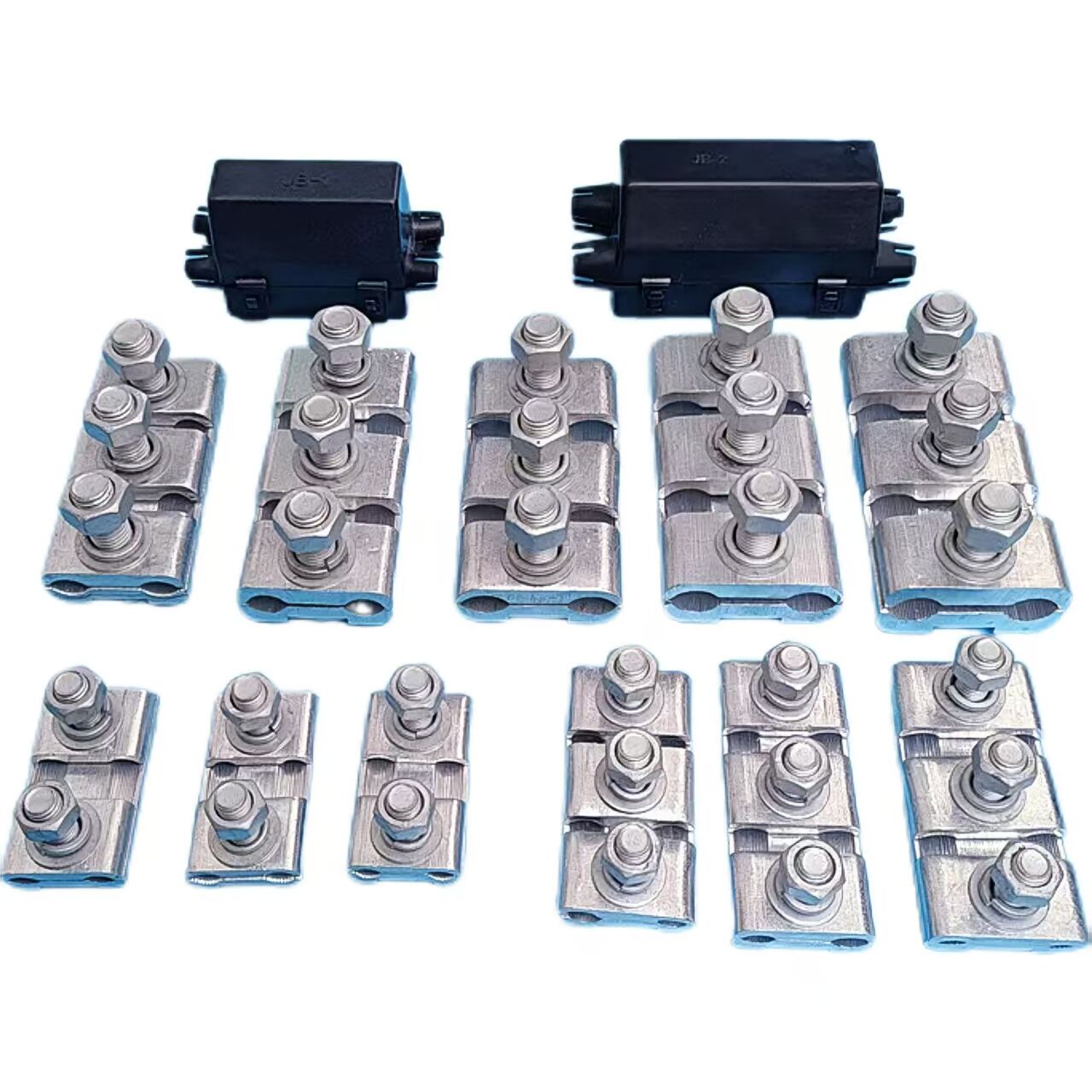
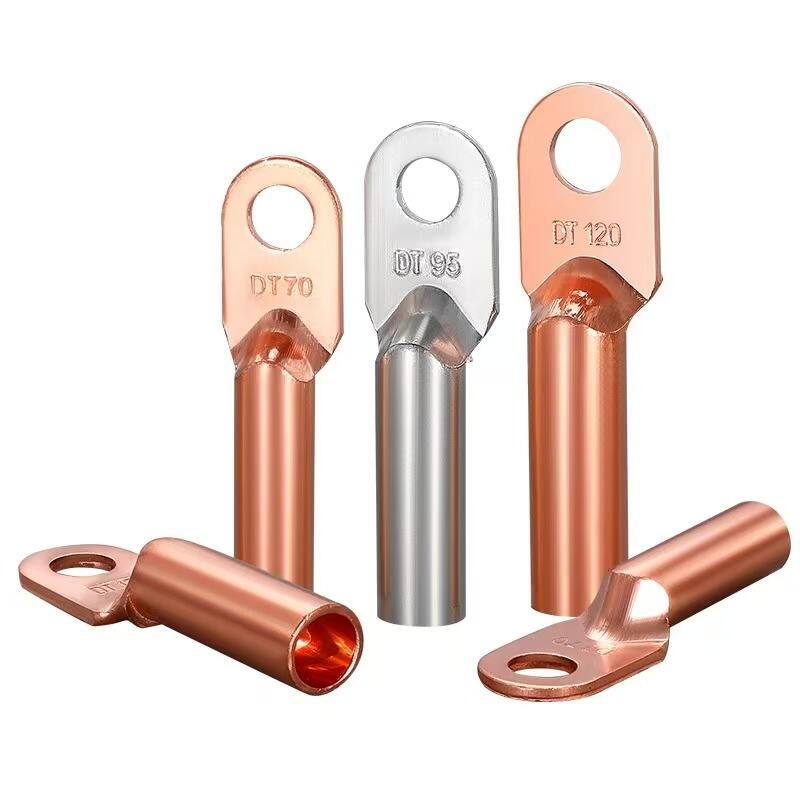
1.High-strength materials
Usually made of high-quality aluminum alloy or high-strength steel, featuring high strength and hardness. They can withstand the gravity and tension of busbars, as well as the electrodynamic forces generated during short circuits, ensuring firm fixation of busbars.
2.Good electrical conductivity
Materials such as aluminum alloy offer excellent electrical conductivity, reducing power loss at the fittings' connection points and preventing performance degradation of the fittings due to heat generation.
3.Corrosion resistance
The surface is treated with anti-corrosion measures such as galvanizing, nickel plating, or coating with anti-corrosion layers, providing strong resistance to corrosion. This enables the fittings to adapt to various outdoor environments and prolongs their service life.
4.Compact structure
With a compact design, they occupy minimal space, effectively utilizing busbar installation space while facilitating installation and maintenance.
 E-mail:
E-mail: